Modern construction and laboratory environments demand materials that deliver exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and longevity. While traditional wood panels have served various applications for decades, phenolic boards have emerged as a superior alternative for specialized environments requiring enhanced performance characteristics. These engineered materials represent a significant advancement in surface technology, offering properties that far exceed what conventional wood can provide in demanding applications.

Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Phenolic Board Construction Technology
Phenolic boards utilize advanced resin technology that combines phenolic resins with reinforcing materials under high temperature and pressure conditions. This manufacturing process creates a dense, non-porous surface that exhibits remarkable resistance to chemicals, moisture, and physical impact. The cross-linked polymer structure forms during the curing process, resulting in a material that maintains its integrity even under extreme conditions. Unlike traditional wood panels that rely on natural fiber orientation, phenolic boards achieve their strength through engineered molecular bonding.
The production methodology involves layering kraft paper or fabric substrates with phenolic resin, then subjecting the assembly to temperatures exceeding 300 degrees Fahrenheit under pressures of several hundred pounds per square inch. This process eliminates voids and creates a homogeneous material with consistent properties throughout its thickness. The resulting product demonstrates superior dimensional stability compared to wood panels, which can warp, crack, or delaminate when exposed to environmental stresses.
Traditional Wood Panel Composition
Traditional wood panels encompass various engineered wood products including plywood, particleboard, medium-density fiberboard, and oriented strand board. These materials rely on wood fibers or particles bonded with adhesives, typically formaldehyde-based resins or polyurethane compounds. The manufacturing process involves pressing wood elements together under controlled temperature and pressure, though at significantly lower levels than those used for phenolic boards production.
Wood panels inherit the natural characteristics of their constituent materials, including grain orientation, moisture sensitivity, and organic composition that makes them susceptible to biological degradation. While surface treatments and laminates can improve performance, the underlying wood substrate continues to influence the panel's behavior under various environmental conditions. The adhesive systems used in wood panel production, while effective for many applications, cannot match the chemical inertness achieved by phenolic resin systems.
Performance Characteristics and Durability
Chemical Resistance Properties
One of the most significant advantages of phenolic boards lies in their exceptional chemical resistance capabilities. These materials can withstand exposure to acids, bases, solvents, and other aggressive chemicals without degradation, making them ideal for laboratory countertops, chemical processing facilities, and industrial applications. The phenolic resin matrix creates a barrier that prevents chemical penetration, maintaining structural integrity even after prolonged exposure to corrosive substances.
Traditional wood panels, conversely, exhibit limited chemical resistance due to their organic composition and porous structure. Even when treated with protective coatings, wood panels can suffer damage from chemical spills, leading to staining, swelling, or structural failure. The adhesives used in wood panel construction may also react with certain chemicals, compromising the bond between layers and reducing overall panel integrity. This fundamental difference makes phenolic boards the preferred choice for environments where chemical exposure is a concern.
Moisture and Environmental Stability
Moisture management represents another critical performance differentiator between these material categories. Phenolic boards demonstrate excellent dimensional stability across varying humidity levels, maintaining their shape and surface characteristics even in high-moisture environments. The non-porous surface prevents water absorption, eliminating issues such as swelling, warping, or delamination that commonly affect wood-based products.
Wood panels, being hygroscopic materials, naturally absorb and release moisture in response to environmental conditions. This behavior can lead to dimensional changes, surface irregularities, and potential failure of adhesive bonds over time. Even moisture-resistant treatments cannot completely eliminate these characteristics, as the underlying wood structure remains susceptible to humidity fluctuations. The differential expansion and contraction of wood fibers can create internal stresses that compromise long-term performance.
Application Suitability and Performance Requirements
Laboratory and Healthcare Environments
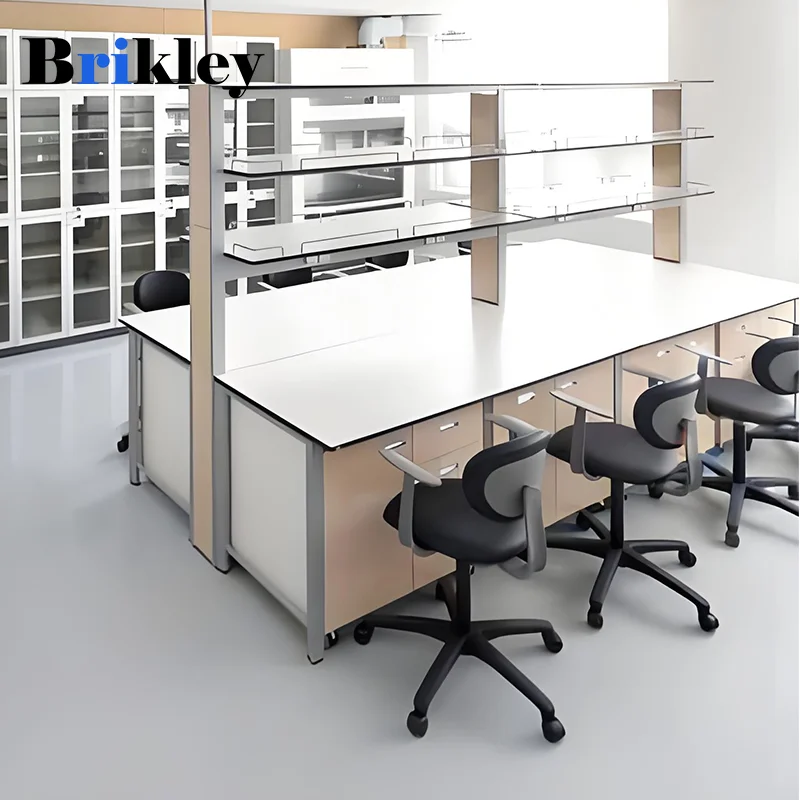
Laboratory applications demand materials that can withstand rigorous cleaning protocols, chemical spills, and sterile conditions without compromising performance or safety. Phenolic boards excel in these environments due to their non-porous surface that resists bacterial growth and facilitates thorough cleaning and disinfection. The material's resistance to common laboratory chemicals, including acids, bases, and organic solvents, ensures reliable performance throughout extended service periods.
Healthcare facilities similarly benefit from phenolic board properties, particularly in areas requiring frequent sanitization and chemical cleaning. The material's ability to maintain its appearance and functionality despite repeated exposure to disinfectants makes it an excellent choice for countertops, cabinetry, and wall panels in medical environments. Traditional wood panels cannot provide the same level of chemical resistance and cleanliness required in these critical applications.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
Industrial environments often subject materials to harsh conditions including temperature extremes, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. Phenolic boards demonstrate superior performance in manufacturing facilities, chemical processing plants, and food preparation areas where hygiene and durability are paramount. The material's resistance to impact damage and surface wear ensures consistent performance even under heavy use conditions.
Commercial applications benefit from phenolic boards' aesthetic versatility and maintenance advantages. Available in numerous colors and surface textures, these materials can meet design requirements while providing superior performance compared to traditional alternatives. The reduced maintenance requirements and extended service life often result in lower total ownership costs despite higher initial material investments.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Initial Investment Considerations
The upfront cost of phenolic boards typically exceeds that of traditional wood panels, reflecting the advanced manufacturing processes and superior material properties. However, this initial premium must be evaluated within the context of total project costs, including installation, finishing, and long-term maintenance requirements. Phenolic boards often require minimal surface preparation and can be installed directly without additional treatments or protective coatings.
Wood panels may appear more economical initially, but additional costs for moisture barriers, surface treatments, edge sealing, and protective finishes can significantly impact the total project budget. Furthermore, the need for more frequent replacement or refinishing of wood panels in demanding environments must be factored into the overall cost analysis. The labor costs associated with surface preparation and finishing can also add substantially to the total installation expense.
Lifecycle Cost Benefits
Long-term value analysis reveals significant advantages for phenolic boards in applications requiring durability and chemical resistance. The extended service life, reduced maintenance requirements, and superior performance characteristics often result in lower total ownership costs over the material's lifespan. Facilities using phenolic boards typically experience fewer disruptions due to material replacement or repair, leading to improved operational efficiency.
The maintenance advantages of phenolic boards become particularly evident in high-use environments where traditional materials would require frequent attention. The non-porous surface resists staining and can be cleaned with standard cleaning products without special precautions or procedures. This translates to reduced maintenance labor costs and fewer operational interruptions compared to wood panel installations that may require periodic refinishing or replacement.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Installation Methodology
Installation of phenolic boards requires specific techniques and considerations that differ from traditional wood panel installation. The material's density and hardness necessitate carbide-tipped cutting tools and specialized drilling equipment to achieve clean, precise cuts. Proper support structures must be engineered to accommodate the material's weight and ensure adequate load distribution across the supporting framework.
Joining methods for phenolic boards include mechanical fastening, adhesive bonding, and welded seam techniques, depending on the specific application requirements. The non-porous nature of the material requires careful selection of adhesives and sealants to ensure proper bonding and long-term performance. Installation teams must be trained on proper handling techniques to prevent damage during transport and installation phases.
Maintenance Protocols and Procedures
Maintenance of phenolic boards involves straightforward cleaning procedures using standard commercial cleaning products. The non-porous surface prevents absorption of spills and contaminants, allowing for easy cleanup of most substances. Regular cleaning with mild detergents and water maintains the material's appearance and hygienic properties without requiring specialized products or procedures.
Traditional wood panels require more complex maintenance protocols, including periodic inspection for moisture damage, surface refinishing, and edge sealing maintenance. The porous nature of wood materials necessitates immediate attention to spills and may require specialized cleaning products to prevent staining or damage. Regular maintenance schedules must account for seasonal dimensional changes and potential structural adjustments.
FAQ
What makes phenolic boards superior to wood panels in laboratory environments
Phenolic boards offer exceptional chemical resistance, non-porous surfaces that prevent bacterial growth, and dimensional stability that wood panels cannot match. Their ability to withstand acids, bases, and solvents without degradation makes them ideal for laboratory applications where chemical spills are common. The easy-to-clean surface maintains hygienic conditions required in research and healthcare facilities.
How do the long-term costs compare between phenolic boards and traditional wood panels
While phenolic boards require higher initial investment, their extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements often result in lower total ownership costs. Wood panels may need replacement or refinishing every few years in demanding environments, while phenolic boards can maintain their performance for decades with minimal maintenance. The reduced downtime and labor costs for repairs make phenolic boards more economical over their lifecycle.
Can phenolic boards be used in residential applications where wood panels are typically specified
Phenolic boards can replace wood panels in residential applications requiring superior durability and chemical resistance, such as kitchen countertops, bathroom surfaces, and utility rooms. However, the higher cost and industrial appearance may not be suitable for all residential design preferences. The decision should consider the specific performance requirements and aesthetic goals of the project.
What installation considerations are unique to phenolic board systems
Installation of phenolic boards requires carbide-tipped tools for cutting and drilling, adequate structural support for the material's weight, and proper selection of adhesives for bonding. The installation team must understand the material's properties to prevent damage during handling and ensure proper joint sealing. Professional installation is recommended to achieve optimal performance and longevity of the system.
Table of Contents
- Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
- Performance Characteristics and Durability
- Application Suitability and Performance Requirements
- Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
- Installation and Maintenance Requirements
-
FAQ
- What makes phenolic boards superior to wood panels in laboratory environments
- How do the long-term costs compare between phenolic boards and traditional wood panels
- Can phenolic boards be used in residential applications where wood panels are typically specified
- What installation considerations are unique to phenolic board systems