Phenolic board stands as one of the most durable and versatile materials in laboratory and industrial applications, offering exceptional chemical resistance and mechanical strength. Understanding proper maintenance protocols is essential for maximizing the lifespan and performance of this engineered composite material. With proper care and attention, phenolic board installations can deliver decades of reliable service while maintaining their structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
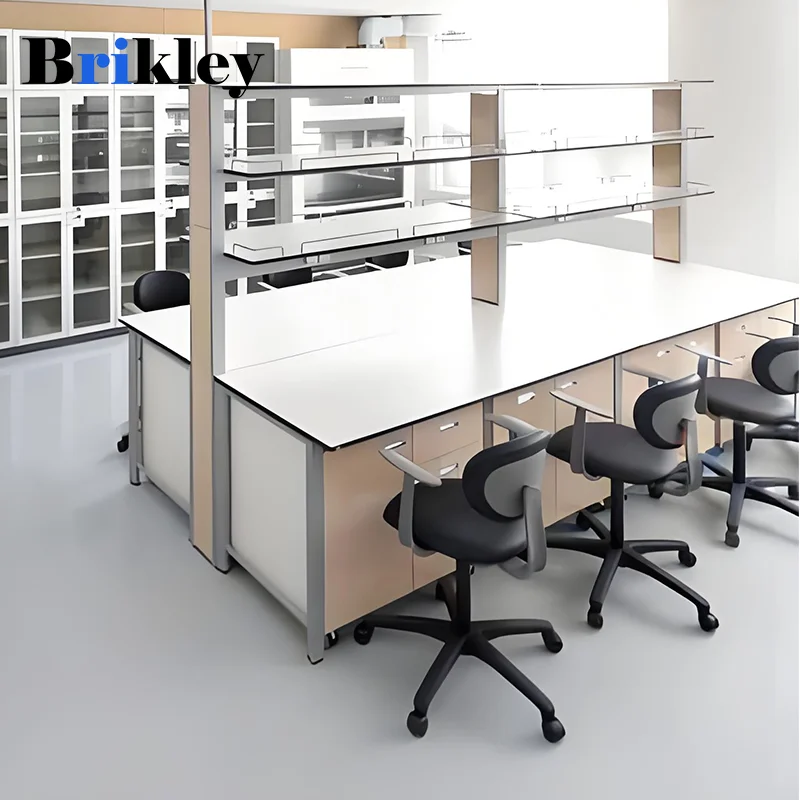

The longevity of phenolic board depends heavily on implementing systematic maintenance practices from the moment of installation. These resin-impregnated materials require specific care protocols that differ significantly from other surface materials commonly found in laboratories and commercial facilities. Regular maintenance not only preserves the material's functional properties but also ensures compliance with safety standards and regulatory requirements.
Understanding Phenolic Board Composition and Properties
Core Material Structure
Phenolic board construction involves multiple layers of kraft paper or fabric impregnated with phenolic resin, creating a thermoset composite with remarkable durability characteristics. The manufacturing process subjects these materials to high temperature and pressure conditions, resulting in a dense, non-porous surface that resists moisture penetration and chemical attack. This fundamental understanding helps facility managers develop appropriate maintenance strategies tailored to the material's unique properties.
The cross-linked polymer structure of phenolic board provides inherent resistance to most acids, bases, and organic solvents commonly encountered in laboratory environments. However, this resistance is not absolute, and certain aggressive chemicals can cause gradual degradation if proper protective measures are not implemented. Understanding these limitations guides maintenance personnel in selecting appropriate cleaning agents and protection protocols.
Surface Characteristics and Vulnerabilities
While phenolic board exhibits excellent overall durability, certain surface characteristics require specific attention during maintenance operations. The material's relatively low surface energy makes it naturally resistant to staining and contamination, but microscopic surface irregularities can trap particulates and chemicals over time. Regular cleaning prevents the accumulation of these contaminants, which could otherwise lead to permanent discoloration or surface etching.
Temperature fluctuations can cause expansion and contraction in phenolic board installations, potentially affecting joint integrity and surface planarity. Maintenance protocols must account for these thermal movements, ensuring that sealing compounds and edge treatments remain effective over time. Proper environmental control and monitoring help minimize these thermal stresses and extend material lifespan.
Daily Cleaning and Surface Care Protocols
Routine Surface Cleaning Procedures
Daily maintenance of phenolic board surfaces begins with thorough removal of all debris, spills, and residual materials using appropriate cleaning solutions. Mild detergents mixed with warm water provide effective cleaning for most applications, while maintaining compatibility with the resin matrix. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or scouring pads that could damage the surface finish and compromise chemical resistance properties.
Immediate spill response is crucial for maintaining phenolic board integrity, particularly when dealing with concentrated acids, strong bases, or organic solvents. Even chemical-resistant materials can experience degradation if aggressive substances remain in contact with surfaces for extended periods. Prompt cleanup using appropriate neutralizing agents and absorbent materials prevents chemical penetration and potential surface damage.
Disinfection and Sanitization Methods
Laboratory and healthcare applications often require regular disinfection of phenolic board surfaces using approved antimicrobial agents. Common disinfectants such as isopropyl alcohol, quaternary ammonium compounds, and diluted bleach solutions are generally compatible with phenolic resin surfaces. However, prolonged exposure to high concentrations of oxidizing agents can cause gradual surface degradation, necessitating careful attention to contact times and concentrations.
Proper disinfection protocols involve applying the sanitizing agent, allowing appropriate contact time for microbial kill, and thoroughly rinsing with clean water to remove residual chemicals. This rinsing step is particularly important when using chlorine-based disinfectants, as residual chlorine can gradually attack the resin matrix over extended periods. Documentation of disinfection procedures helps ensure consistency and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Environmental Control and Monitoring
Maintaining stable environmental conditions significantly extends phenolic board service life by minimizing thermal and moisture-related stresses. Temperature fluctuations should be kept within reasonable limits, typically between 60-80°F, to prevent excessive expansion and contraction cycles. Humidity control is equally important, as extreme moisture conditions can affect adhesive bonds and joint integrity in multi-panel installations.
Regular monitoring of environmental conditions using calibrated instruments helps identify potential problems before they impact phenolic board performance. Data logging systems can track temperature and humidity trends, alerting maintenance personnel to conditions that might accelerate material degradation. This proactive approach enables timely intervention and prevents costly repairs or replacements.
Protective Coatings and Treatments
While phenolic board possesses inherent chemical resistance, applying protective treatments can enhance durability in particularly aggressive environments. Specialized sealers designed for laboratory surfaces can provide additional protection against chemical attack while maintaining the material's natural properties. These treatments typically require periodic renewal based on usage patterns and environmental conditions.
Selection of appropriate protective treatments depends on specific application requirements and chemical exposure profiles. Some facilities benefit from anti-static treatments that reduce dust accumulation, while others require enhanced stain resistance for high-traffic areas. Consultation with material suppliers and coating manufacturers ensures optimal treatment selection and application procedures.
Long-term Preservation Techniques
Structural Integrity Assessment
Periodic inspection of phenolic board installations should include assessment of structural integrity, joint conditions, and attachment systems. Look for signs of delamination, edge chipping, or surface cracking that might indicate material fatigue or improper installation. Early detection of these issues allows for targeted repairs that prevent more extensive damage and maintain overall system performance.
Joint inspection is particularly important in large installations where multiple phenolic board panels are connected using mechanical fasteners or adhesive systems. Check for signs of movement, separation, or sealant failure that could allow moisture or chemical penetration. Proper joint maintenance prevents water damage and maintains the hygienic properties essential for laboratory applications.
Repair and Restoration Methods
Minor surface damage to phenolic board can often be repaired using specialized compounds and restoration techniques that restore both appearance and functionality. Small chips or scratches may be filled with compatible repair materials, while more extensive damage might require panel replacement or professional restoration services. Prompt attention to minor damage prevents propagation and maintains the material's protective properties.
Professional restoration services can address more significant damage through processes such as surface refinishing, chemical etching removal, and structural repairs. These services typically involve specialized equipment and materials designed specifically for phenolic resin systems. Cost-benefit analysis helps determine when restoration is preferable to replacement, considering factors such as extent of damage, age of installation, and performance requirements.
Chemical Compatibility and Storage Considerations
Chemical Exposure Management
Understanding chemical compatibility is essential for maintaining phenolic board performance in laboratory and industrial environments. While these materials resist most common chemicals, certain substances can cause gradual degradation or immediate damage if not properly managed. Maintain updated compatibility charts and ensure that all personnel understand proper handling procedures for potentially damaging chemicals.
Implement protocols for handling concentrated acids, strong oxidizing agents, and organic solvents that might affect phenolic board surfaces. These procedures should include requirements for immediate cleanup, use of appropriate containment measures, and regular inspection for signs of chemical damage. Training programs help ensure that all personnel understand these requirements and implement them consistently.
Storage and Handling Best Practices
Proper storage of maintenance supplies and chemicals used near phenolic board surfaces requires careful attention to compatibility and safety considerations. Store cleaning agents, disinfectants, and repair materials in appropriate containers and locations that prevent accidental spills or contamination. Secondary containment systems provide additional protection against storage-related accidents.
Handling procedures for items placed on phenolic board surfaces should minimize potential damage from heavy objects, sharp tools, or abrasive materials. Use protective pads or covers when necessary, and establish protocols for moving equipment or materials that might scratch or damage the surface. These precautions help preserve the material's appearance and functional properties over its service life.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Surface Staining and Discoloration
Surface staining on phenolic board typically results from prolonged contact with certain chemicals, inadequate cleaning procedures, or use of inappropriate cleaning agents. Most stains can be removed using specialized cleaning compounds designed for resin surfaces, though some discoloration may be permanent if the staining agent has penetrated the surface layer. Prevention through prompt spill cleanup and proper chemical handling remains the most effective approach.
Persistent stains may require more aggressive cleaning techniques, including use of mild abrasives or specialized stain removal products. However, these methods should be used cautiously to avoid damaging the surface finish. Test any aggressive cleaning method in an inconspicuous area before applying it to visible surfaces, and follow manufacturer recommendations for product selection and application procedures.
Edge and Joint Problems
Edge chipping and joint separation represent common issues in phenolic board installations, often resulting from thermal movement, mechanical stress, or inadequate initial installation. Address these problems promptly to prevent water penetration and maintain the hygienic properties essential for laboratory applications. Edge repairs typically involve careful removal of damaged material and application of compatible repair compounds.
Joint maintenance requires attention to sealant condition, fastener integrity, and panel alignment. Replace deteriorated sealants using products specifically designed for phenolic board applications, ensuring proper surface preparation and curing conditions. Monitor joint performance over time, as thermal cycling and structural movements can affect long-term integrity even in properly installed systems.
FAQ
How often should phenolic board surfaces be deep cleaned
Deep cleaning of phenolic board surfaces should be performed weekly or bi-weekly depending on usage intensity and environmental conditions. High-traffic laboratory areas may require more frequent deep cleaning, while storage or low-use areas can be maintained with less frequent intensive cleaning. The key is maintaining consistency and adjusting frequency based on actual contamination levels and appearance standards.
Can phenolic board be refinished if the surface becomes damaged
Yes, phenolic board can often be refinished through professional restoration services that can address surface scratches, chemical etching, and minor structural damage. The process typically involves careful surface preparation, application of compatible repair materials, and refinishing to match the original appearance. However, extensive damage may require panel replacement rather than refinishing.
What cleaning products should be avoided on phenolic board
Avoid using strong alkaline cleaners, concentrated bleach solutions, abrasive scouring compounds, and organic solvents for routine cleaning of phenolic board. These substances can cause surface damage, discoloration, or gradual degradation of the resin matrix. Stick to mild detergents, approved disinfectants, and specialized cleaners designed for laboratory surfaces to ensure long-term material performance.
How can I tell if phenolic board needs replacement rather than repair
Consider replacement when phenolic board shows extensive delamination, structural damage that affects integrity, widespread chemical damage, or surface degradation that cannot be restored. Other indicators include repeated joint failures, inability to maintain hygienic standards, or damage that affects the material's chemical resistance properties. Professional assessment can help determine whether repair or replacement is the most cost-effective approach.